Recent Research Topics 最近の研究テーマ
(日本語は google 翻訳)
1. Acid induced folding by HP-ESI 強酸誘導タンパク質の折り畳み
Probing Acid-Induced Compaction of Denatured Proteins by High-Pressure Electrospray Mass Spectrometry
高圧エレクトロスプレー質量分析による変性タンパク質の酸誘起圧縮
Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 39, 14816–14821

Summary
Further increase in the acidity in the most denaturing acidic solution is known to induce compaction of the fully unfolded protein into a compact molten globule. The phenomenon of “acid-induced folding of proteins” takes place at pH ∼1 in strong acid aqueous solutions with high electrical conductivity and surface tension, a condition that is difficult to handle using conventional electrospray ionization methods for mass spectrometry. Here, high-pressure electrospray ionization (HP-ESI) is used to produce well-resolved mass spectra for proteins in strong acids with pH as low as 1. The compaction of protein conformation is indicated by a large shift in the charge state from high charges to native-like low charges. The addition of salt to the protein in the most denaturing condition also reproduces the compaction effect, thereby supporting the role of anions in this phenomenon. Similar compaction of proteins is also observed in organic solvent/acid mixtures. The charge state of the compacted protein depends on the type of anions that formed ion pairs with a positive charge on the protein. The dissociation of ion pairs during the ionization process forms neutral acids that can be observed by HP-ESI using a soft ion introduction configuration.
要旨
最も変性性の高い酸性溶液中での酸性度のさらなる増加は、完全に折り畳まれていないタンパク質のコンパクトな溶融小球への圧縮を誘導することが知られている。 「酸によるタンパク質のフォールディング」現象は、高い電気伝導率と表面張力を持つ強酸水溶液中で pH ~ 1 で起こりますが、この条件は質量分析用の従来のエレクトロスプレー イオン化法を使用して処理するのが困難です。ここでは、高圧エレクトロスプレー イオン化 (HP-ESI) を使用して、pH 1 程度の強酸中でタンパク質の高分解能の質量スペクトルを生成します。タンパク質の立体構造の圧縮は、高い電荷状態からの大きな電荷状態のシフトによって示されます。ネイティブのような低料金に請求します。最も変性が進んだ状態でタンパク質に塩を加えると圧縮効果が再現され、それによってこの現象におけるアニオンの役割が裏付けられます。同様のタンパク質の圧縮は、有機溶媒と酸の混合物でも観察されます。圧縮されたタンパク質の電荷状態は、タンパク質上で正電荷を持つイオンペアを形成するアニオンの種類によって異なります。イオン化プロセス中のイオンペアの解離により中性酸が形成され、ソフトイオン導入構成を使用した HP-ESI で観察できます。
2. Feedback Control for ESI
Feedback Control of Electrospray with and without an External Liquid Pump Using the Spray Current and the Apex Angle of a Taylor Cone for ESI-MS
ESI-MS 用のスプレー電流とテイラー コーンの頂角を使用した、外部液体ポンプを使用する場合と使用しない場合のエレクトロスプレーのフィードバック制御
Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 28, 10744–10751

Summary
An electrospray operated in the steady cone-jet mode is highly stable but the operating state can shift to pulsation or multijet modes owing to changes in flow rate, surface tension, and electrostatic variables. Here, a simple feedback control system was developed using the spray current and the apex angle of a Taylor cone to determine the error signal for correcting the emitter voltage. The system was applied to lock the cone-jet mode operation against external perturbations. For a pump-driven electrospray at a regulated flow rate, the apex angle of the Taylor cone decreased with increasing voltage. In contrast, for a voltage-driven electrospray with low flow resistance, the angle was found to increase with the emitter voltage. A simple algorithm based on iterative learning control was formulated and implemented using a personal computer to automatically correct the emitter voltage in response to the error signal. For voltage-driven electrospray ionization (ESI), the feedback control of the spray current can also be used to regulate the flow rate to an arbitrary value or pattern. Electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) with feedback control was demonstrated to produce ion signal acquisition with long-term stability that was insusceptible to the emulated external disturbances.
要旨
ESI-MS 用のスプレー電流とテイラー コーンの頂角を使用した、外部液体ポンプを使用する場合と使用しない場合のエレクトロスプレーのフィードバック制御定常コーンジェット モードで動作するエレクトロスプレーは非常に安定していますが、動作状態が脈動モードまたはマルチジェット モードに移行する可能性があります。 流量、表面張力、静電変数の変化によるものです。 ここでは、スプレー電流とテイラーコーンの頂角を使用して、エミッタ電圧を補正するための誤差信号を決定する簡単なフィードバック制御システムが開発されました。 このシステムは、外部摂動に対してコーンジェット モードの動作をロックするために適用されました。 調整された流量でのポンプ駆動のエレクトロスプレーの場合、テイラーコーンの頂角は電圧の増加とともに減少しました。 対照的に、流れ抵抗が低い電圧駆動のエレクトロスプレーの場合、角度はエミッター電圧とともに増加することがわかりました。 誤差信号に応じてエミッタ電圧を自動的に補正するため、反復学習制御に基づいた簡単なアルゴリズムをパーソナルコンピュータを使用して定式化および実装しました。 電圧駆動のエレクトロスプレーイオン化 (ESI) の場合、スプレー電流のフィードバック制御を使用して、流量を任意の値またはパターンに調整することもできます。 フィードバック制御を備えたエレクトロスプレーイオン化質量分析法 (ESI-MS) は、エミュレートされた外部擾乱の影響を受けにくい長期安定性を備えたイオン信号取得を生成することが実証されました。
3. Zip Tip nanoESI
Characteristics of high-pressure nanoESI-MS using standard and chromatographically packed (ZipTip) micropipette tips as emitters for highly conductive solutions
標準マイクロピペットチップとクロマトグラフィーパック (ZipTip) マイクロピペットチップを高導電性溶液のエミッターとして使用する高圧 nanoESI-MS の特性
Int. J. Mass Spectrom, 2023, Vol 492, pp 117118
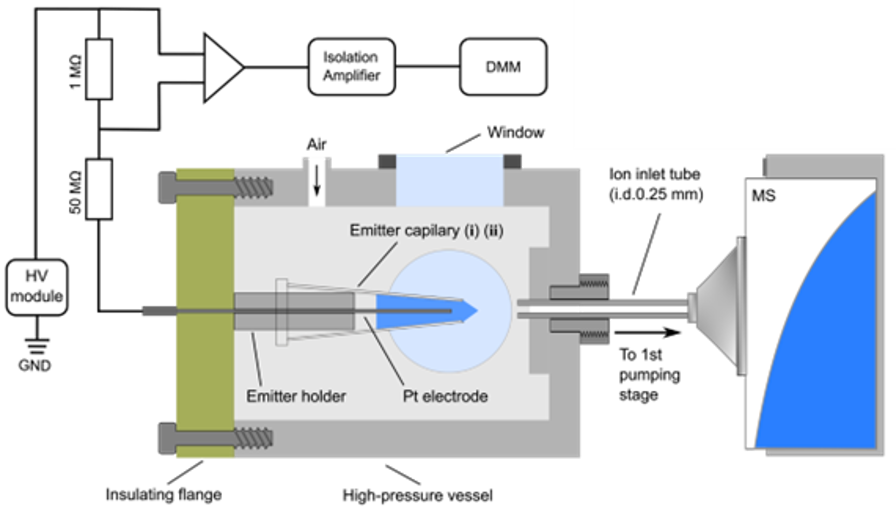

Summary
Voltage-driven electrospray of highly conductive solutions under high pressure without gaseous breakdown enabled a low flow rate nanoESI using an emitter of large inner diameters such as a commercial micropipette tip. This feature was previously exploited to observe unique ionization responses at flow rates close to their minimum values (Chem. Sci. 14, 4506–4515 & Anal. Chem. 94, 16,015–16022). Here, we studied the properties of such pipet tip sprayers at a higher spray current up to >2 μA with flow rates approaching their maximum values. Normal pipet tips with 0.37 mm i.d. and tips packed with chromatographic particles (ZipTip, i.d. 0.44 mm) were used. The nanoflow rate was tuned using emitter voltage with spray current as the monitoring signal for flow rate. The spray current and flow rate relationship followed the law for < 1 μA. Above that point, the Taylor cone was still stable but the spray current increased at a higher rate with the flow rate. The packed pipet tips have a larger flow resistivity, required a higher onset voltage, and interestingly, supported a higher stable spray current and flow rate. HP-nanoESI-MS of protein and oligosaccharide showed variation in charge state and ion intensity with the spray current. The direct nanoESI of extraction solution from the ZipTip right after the desalting and concentrating procedures were also demonstrated.
要旨
ガスの破壊を伴わない高圧下での高導電性溶液の電圧駆動エレクトロスプレーにより、市販のマイクロピペットチップなどの大きな内径のエミッターを使用した低流量のナノESIが可能になりました。この機能は、以前、最小値に近い流量での固有のイオン化応答を観察するために利用されていました (Chem. Sci. 14, 4506–4515 & Anal. Chem. 94, 16,015–16022)。ここでは、最大値に近い流量で最大 2 μA までの高いスプレー電流でのこのようなピペット チップ スプレーの特性を研究しました。内径 0.37 mm の通常のピペットチップクロマトグラフィー粒子を詰めたチップ (ZipTip、内径 0.44 mm) を使用しました。ナノ流量は、流量の監視信号としてスプレー電流とともにエミッタ電圧を使用して調整されました。スプレー電流と流量関係は続いた~のための法則 < 1μA。その点を超えると、テイラー コーンは依然として安定していましたが、スプレー流は流量とともにより高い割合で増加しました。充填されたピペットチップは、より大きな流れ抵抗率を持ち、より高い開始電圧を必要とし、興味深いことに、より安定したスプレー電流と流量をサポートします。タンパク質とオリゴ糖の HP-nanoESI-MS は、スプレー電流に応じて荷電状態とイオン強度が変化することを示しました。脱塩および濃縮手順直後の ZipTip からの抽出溶液の直接 nanoESI も実証されました。
4. Tuning Oxidation by Electric Field
Tuning oxidative modification by a strong electric field using nanoESI of highly conductive solutions near the minimum flow rate
最小流量付近の高導電性溶液の nanoESI を使用した強電場による酸化修飾の調整
Chem. Sci., 2023, vol 14, pp 4506-4515
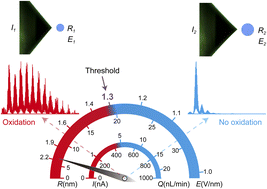
Summary
Oxidative modification is usually used in mass spectrometry (MS) for labeling and structural analysis. Here we report a highly tunable oxidation that can be performed in line with the nanoESI-MS analysis at the same ESI emitter without the use of oxidative reagents such as ozone and H2O2, and UV activation. The method is based on the high-pressure nanoESI of a highly conductive (conductivity >3.8 S m−1) aqueous solution near the minimum flow rate. The ion source is operated under super-atmospheric pressure (0.5 MPa gauge pressure) to avoid the contribution of electric discharge. The analyte at the tip of the Taylor cone or in the emitter droplet can be locally oxidized in an on-demand manner by varying the nanoflow rate. With an offline nanoESI, the degree of oxidation, i.e., the average number of incorporated oxygen atoms, can be finely tuned by voltage modulation using spray current as the feedback signal. Oxidations of easily oxidized residues present in peptides/proteins and the double bonds of the unsaturated phosphatidylcholine occur at low flow rate operation (<5 nL min−1) when the electric field at the tip of the Taylor cone and the initially produced charged droplet reaches approximately 1.3 V nm−1. The oxidized ion signal responds instantaneously to changes in flow rate, indicating that the oxidation is highly localized. Using isotope labeling, it was found that the incorporated oxygen primarily originates from the gas phase, suggesting a direct oxidation pathway for the analyte enriched on the liquid surface via the reactive oxygen atoms formed by the strong electric field.
要旨
酸化修飾は通常、標識および構造分析のための質量分析 (MS) で使用されます。 今回我々は、オゾンやH2O2などの酸化試薬やUV活性化を使用せずに、同じESIエミッターでのnanoESI-MS分析に沿って実行できる、高度に調整可能な酸化を報告します。 この方法は、最小流量に近い高導電性 (導電率 >3.8 S m-1) 水溶液の高圧ナノ ESI に基づいています。 イオン源は、放電の影響を避けるために超大気圧 (0.5 MPa ゲージ圧) の下で動作します。 テイラーコーンの先端またはエミッター液滴内の検体は、ナノ流量を変化させることによってオンデマンド方式で局所的に酸化できます。 オフライン nanoESI を使用すると、スプレー電流をフィードバック信号として使用する電圧変調によって、酸化の度合い、つまり取り込まれた酸素原子の平均数を微調整できます。 ペプチド/タンパク質に存在する酸化されやすい残基と不飽和ホスファチジルコリンの二重結合の酸化は、テイラーコーンの先端と最初に生成された荷電液滴の電場が到達したときに、低流量操作 (<5 nL min-1) で発生します。 約1.3Vnm−1。 酸化イオン信号は流量の変化に瞬時に反応し、酸化が高度に局所的に発生していることを示しています。 同位体標識を使用すると、取り込まれた酸素は主に気相に由来することが判明し、強電場によって形成された活性酸素原子を介して、液体表面に濃縮された分析対象物の直接酸化経路が示唆された。
5. Bipolar Electrospray 両極性静電噴霧
Bipolar Electrospray from Electrodeless Emitters for ESI without Electrochemical Reactions in the Sprayer
電気化学反応のない両極性エレクトロスプレー
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 4, 728–736

Summary
A bipolar ESI source is developed to generate a simultaneous emission of charged liquid jets of opposite polarity from an electrodeless sprayer. The sprayer consists of two emitters, and the electrosprays are initiated by applying a high potential difference (HV) across the counter electrodes facing each emitter. The sprayer and the liquid delivery system are made of all insulators without metal components, thus enabling the total elimination of electrochemical reactions taking place at the liquid–electrode interface in the typical electrosprayer. The bipolar electrospray has been implemented using an online configuration that uses a syringe pump for flow rate regulation and an offline configuration that relies on HV for adjusting the flow rate. The voltage–current and flow rate–current relationships of bipolar electrospray were found to be similar to the standard electrospray. The application of bipolar ESI to the mass spectrometry of protein, peptide, and metallocene without electrochemically induced oxidation/reduction is demonstrated.
要旨
バイポーラ ESI ソースは、無電極噴霧器から反対極性の荷電液体ジェットの同時放出を生成するために開発されました。噴霧器は 2 つのエミッターで構成され、エレクトロ スプレーは、各エミッターに面している対電極間に高電位差 (HV) を適用することによって開始されます。噴霧器と液体供給システムは、金属部品を含まないすべての絶縁体でできているため、典型的なエレクトロスプレーの液体と電極の界面で起こる電気化学反応を完全に排除できます。バイポーラ エレクトロ スプレーは、流量調整用のシリンジ ポンプを使用するオンライン構成と、流量を調整するための HV に依存するオフライン構成を使用して実装されています。バイポーラエレクトロスプレーの電圧 - 電流および流量 - 電流の関係は、標準のエレクトロスプレーと同様であることがわかりました。バイポーラ ESI のタンパク質、ペプチド、メタロセンの質量分析への応用が、電気化学的に酸化/還元を誘発しないことが実証されています。
6. Scanning nanoflow ESI ナノ流量の走査
A Subtle Change in Nanoflow Rate Alters the Ionization Response As Revealed by Scanning Voltage ESI-MS
走査電圧 ESI-MS によって明らかにされたように、ナノフロー速度のわずかな変化がイオン化応答を変化させる
Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 46, 16015–16022

Summary
The small charged droplet generated from the nanoelectrospray ionization (nanoESI) source at nL/min flow rate gives its unique feature of high-performance ionization. A continuous scan of the flow rate in this regime can trace the effect of droplet size in greater detail for a better understanding of the ionization process. To date, such practical implementation is hindered by the lack of a suitable liquid pump and the reproducibility of microcapillaries-based systems. Here, offline nanoESI mass spectrometry with a continuously varying flow rate in a dynamic range of several hundred pL/min to ∼100 nL/min was performed by the precision scanning of ESI high voltage (HV). The principle is based on the new paradigm of generating nanoelectrospray from a large Taylor cone with a known spray current–flow rate relationship. The instantaneous flow rate controlled by the HV was determined by simultaneous measurement of the spray current. The system is successfully applied to reveal the role of nanoflow rate on the average charge state of proteins, analysis of analyte mixture, and desalting effect. With the use of a buffer solution with high electric conductivity, a highly controllable oxidative modification was also observed by tuning the flow rate below a threshold of ∼5 nL/min, a finding that has potential application to on-demand oxygen labeling.
要旨
nL/min の流量でナノエレクトロ スプレー イオン化 (nanoESI) ソースから生成された小さな荷電液滴は、高性能イオン化の独自の機能を提供します。この体制での流量の連続スキャンは、イオン化プロセスをよりよく理解するために、液滴サイズの影響をより詳細に追跡できます。今日まで、このような実用的な実装は、適切な液体ポンプの欠如とマイクロキャピラリーベースのシステムの再現性によって妨げられています。ここでは、ESI高電圧(HV)の精密スキャンにより、数百pL / minから〜100 nL / minのダイナミックレンジで連続的に変化する流量でのオフラインnanoESI質量分析が実行されました。この原理は、既知のスプレー電流と流量の関係を持つ大きなテイラーコーンからナノエレクトロスプレーを生成するという新しいパラダイムに基づいています。 HV によって制御される瞬時流量は、スプレー電流の同時測定によって決定されました。このシステムは、タンパク質の平均荷電状態、分析対象混合物の分析、および脱塩効果に対するナノフロー レートの役割を明らかにするためにうまく適用されています。電気伝導度の高い緩衝液を使用すると、流量を約5 nL / minのしきい値未満に調整することにより、高度に制御可能な酸化修飾も観察されました。これは、オンデマンド酸素標識への応用の可能性がある発見です。
7. Taylor Cone テイラーコーン
Generation of Ions from Aqueous Taylor Cones near the Minimum Flow Rate: “True Nanoelectrospray” without Narrow Capillary
最小流量に近い水性テイラーコーンからのイオンの生成:細いキャピラリーを使わない「真のナノエレクトロスプレー」
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 3, 491–498

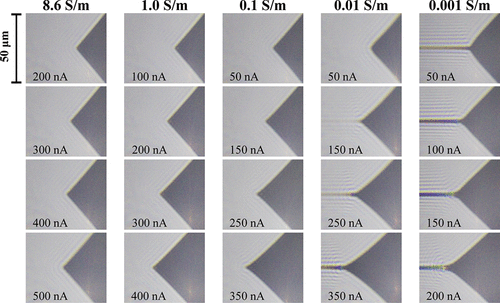
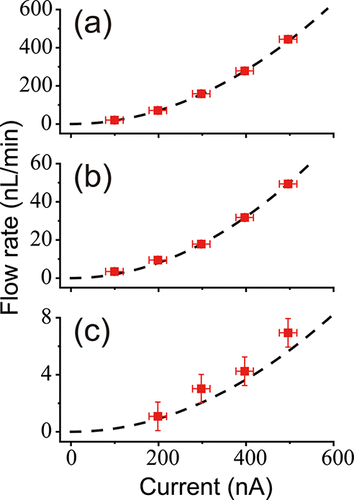
Summary
Generating ultrafine charged droplets using electrospray is crucial for attaining high ionization efficiency for mass spectrometry. The size of the precursor charged droplets depends on the spray flow rate, and conventional wisdom holds that an electrospray of a nL/min flow rate (nanoelectrospray) is only possible using narrow capillaries with an inner diameter of ∼1 μm or smaller. Here, the electrospray of aqueous solutions with high electric conductivities generated from a large off-line capillary of 0.4 mm i.d. has been performed using a high-pressure ion source. The electric discharge is avoided by operating the ion source at 2.5 bar gauge pressure. The highly stable Taylor cone can be tuned to a near-hydrostatic state that exhibits the “true nanoelectrospray” properties, i.e., high salt tolerance and minimal ion suppression. The Q1/2 scaling law describing the electrospray current I and flow rate Q is found to be valid down to the nanoflow regime under a condition that is free of electric discharge. For a given solution, the flow rate and the size of the initial droplets and ionization species can be controlled with the spray current as the indicator for the instantaneous flow rate without changing the emitter capillary of different sizes. In regard to the application, the nanoelectrospray with a large micropipette tip is easy to use, free of clogging when dealing with viscous and high-salt buffer solutions, and with reduced surface interaction with the emitter inner surface. An acquisition of very clean mass spectra of proteins from concentrated solutions of nonvolatile salts such as phosphate-buffered saline is demonstrated.
要旨
エレクトロスプレーを使用して超微細な荷電液滴を生成することは、質量分析の高いイオン化効率を達成するために重要です。前駆体に帯電した液滴のサイズはスプレー流量に依存し、従来の知恵では、nL / minの流量のエレクトロスプレー(ナノエレクトロスプレー)は、内径が約1μm以下の細いキャピラリーを使用した場合にのみ可能であるとされています。ここでは、内径0.4mmの大型オフラインキャピラリーから生成された導電率の高い水溶液のエレクトロスプレー。高圧イオン源を使用して実行されています。イオン源を2.5バールゲージ圧で操作することにより、放電を回避します。非常に安定したテイラーコーンは、「真のナノエレクトロスプレー」特性、つまり高い耐塩性と最小限のイオン抑制を示す静水圧に近い状態に調整できます。エレクトロスプレー電流Iと流量Qを説明するQ1/2スケーリング則は、放電のない条件下でナノフローレジームまで有効であることがわかります。与えられた解決策について、初期液滴とイオン化種の流量とサイズは、異なるサイズのエミッターキャピラリーを変更することなく、瞬間流量の指標としてスプレー電流を使用して制御できます。アプリケーションに関しては、大きなマイクロピペットチップを備えたナノエレクトロスプレーは使いやすく、粘性のある高塩の緩衝液を扱うときに目詰まりがなく、エミッターの内面との表面相互作用が減少しています。リン酸緩衝生理食塩水などの不揮発性塩の濃縮溶液からのタンパク質の非常にクリーンな質量スペクトルの取得が示されています。
8. Protein Charge State タンパク質の平均電荷
High-pressure nanoESI of highly conductive volatile and non-volatile buffer solutions from a large Taylor cone: Effect of spray current on charge state distribution
大きなテイラーコーンからの高導電性揮発性および不揮発性緩衝液の高圧nanoESI:電荷状態分布に対するスプレー電流の影響
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 476, 116845

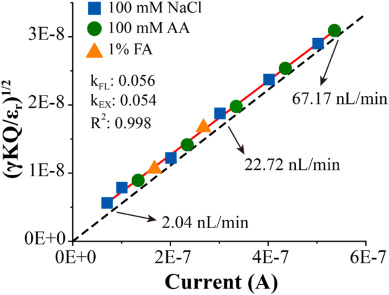
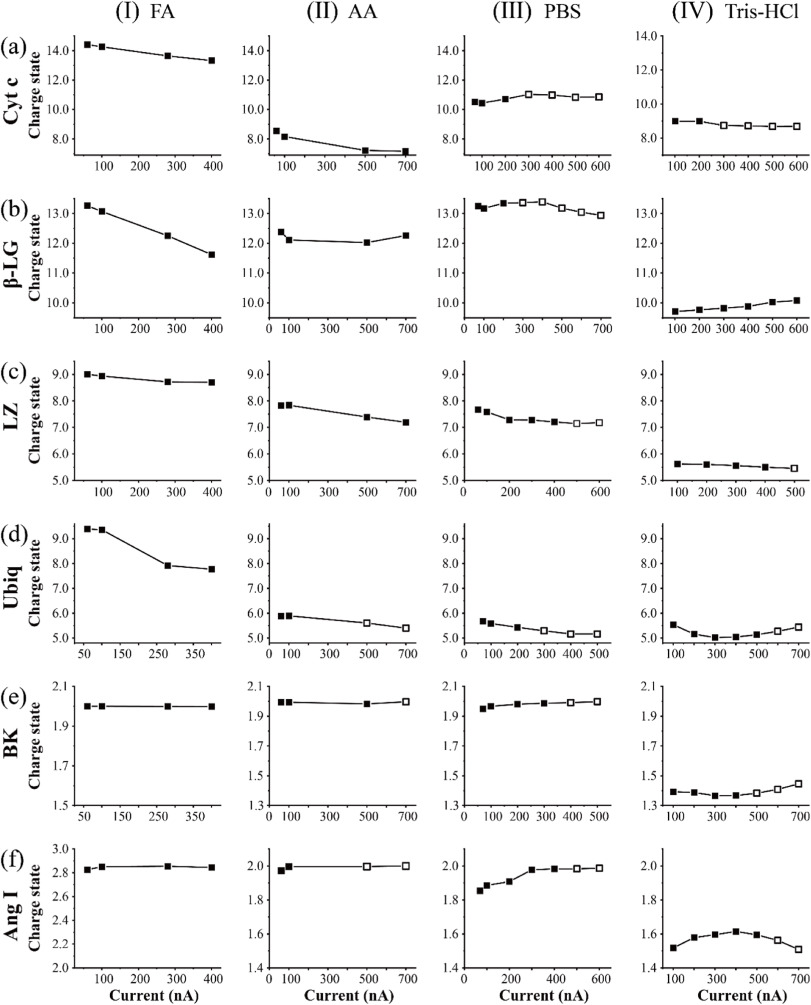
Summary
Direct ESI-MS of proteins in nonvolatile buffer requires the generation of very fine initial droplets to resolve the peak for meaningful analysis. This is usually achieved using nanoESI capillary with an inner diameter of ∼1 μm or smaller. Recently we reported the generation of “true nanoelectrospray” from a micropipette tip with a large inner diameter under the super-atmospheric pressure condition (J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 491–498). The flow rate in the nL/min regime can be reproducibly adjusted using high voltage with the spray current as the indicator for flow rate. Here two further works are done on the same ion source. First, the validation of the spray current-flow rate relationship has been extended to 0.5 MPa, and the achievable minimum spray current is found to reduce with the ion source pressure. Second, the ion source is applied to study the flow rate effect on the charge state distribution in the nanoflow regime for proteins and peptides in volatile (formic acid and ammonium acetate) and the nonvolatile (phosphate buffer saline (PBS) and 1 M Tris-HCl) buffers. For the nonvolatile buffers, clean nanoESI mass spectra are only obtained at a low flow rate of ∼1 nL/min. The average charge state of the tested proteins is primarily determined by the type of buffer. For acidic solutions, the charge state shifts to a higher value at a lower flow rate. For non-denaturing solutions, the average charge number remained relatively constant but the variation with the flow rate appeared to be analyte and buffer dependent.
要旨
不揮発性バッファー中のタンパク質の直接ESI-MSでは、意味のある分析のためにピークを分離するために、非常に微細な初期液滴を生成する必要があります。これは通常、内径が約1μm以下のnanoESIキャピラリーを使用して実現されます。最近、超大気圧条件下で内径の大きいマイクロピペットチップから「真のナノエレクトロスプレー」が生成されることを報告しました(J.Am。Soc。MassSpectrom。2022、33、491–498)。 nL / minレジームの流量は、流量の指標としてスプレー電流を使用して高電圧を使用して再現性よく調整できます。ここでは、同じイオン源でさらに2つの作業が行われます。まず、スプレー電流と流量の関係の検証が0.5 MPaに拡張され、達成可能な最小スプレー電流がイオン源の圧力とともに減少することがわかりました。次に、イオン源を適用して、揮発性(ギ酸および酢酸アンモニウム)および不揮発性(リン酸緩衝生理食塩水(PBS)および1 M Tris- HCl)バッファー。不揮発性バッファーの場合、クリーンなnanoESI質量スペクトルは、約1 nL/minの低流量でのみ取得されます。テストされたタンパク質の平均電荷状態は、主にバッファーのタイプによって決まります。酸性溶液の場合、より低い流量で電荷状態がより高い値にシフトします。非変性溶液の場合、平均電荷数は比較的一定のままでしたが、流量による変動は分析物とバッファーに依存するように見えました。
9. Inlet ESI 毛細管内の静電気噴霧
Electrospray Ionization Inside the Ion Inlet Tube: Multijet Mode Operation
イオン注入管内のエレクトロスプレーイオン化:マルチジェットモード操作
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 32, 7, 1821–1828

Summary
We investigated the electrospray ionization inside the narrow channel of the ion inlet tube. An insulating emitter capillary made of fused silica with a 0.2 mm outer diameter was inserted into the ion inlet tubes with a 0.5 and 0.6 mm inner diameter to aspirate all the charged droplets. A custom-made ion inlet tube with two side holes near its entrance is used to observe the spraying condition. The spray current is measured and monitored during the MS acquisition using isolation amplifiers. Because the emitter is cylindrically surrounded in close proximity by the metallic inner wall, it is difficult to obtain a stable and symmetric Taylor cone with its apex at the center of the emitter. Instead, a stable operation under a flow rate of 1–4 μL/min is found to be in the form of a multicone-jet mode with two or more Taylor cones anchoring around the rim of the emitter. The emitted charged droplet jets are dragged from hitting the wall by the fast-flowing air inside the inlet tube. Comparison with the typical cone-jet and multijet mode operated several millimeters outside the inlet capillary shows signal enhancements for protein standards.
要旨
イオン注入口チューブの狭いチャネル内のエレクトロスプレーイオン化を調査しました。外径0.2mmのフューズドシリカ製の絶縁エミッタキャピラリを、内径0.5mmと0.6mmのイオン注入口チューブに挿入して、帯電したすべての液滴を吸引しました。入口近くに2つの側面穴があるカスタムメイドのイオン注入口チューブを使用して、噴霧状態を観察します。スプレー電流は、アイソレーションアンプを使用してMS取得中に測定および監視されます。エミッターは金属の内壁に近接して円筒状に囲まれているため、エミッターの中心に頂点がある安定した対称のテイラーコーンを得るのは困難です。代わりに、1〜4μL /分の流量での安定した動作は、エミッターの縁の周りに2つ以上のテイラーコーンが固定されたマルチコーンジェットモードの形であることがわかります。放出された帯電液滴ジェットは、インレットチューブ内の高速で流れる空気によって壁に当たらないように引きずられます。注入口キャピラリの数ミリメートル外側で操作される典型的なコーンジェットおよびマルチジェットモードとの比較は、タンパク質標準のシグナル増強を示しています。
10. Endoscopic MS 内視鏡質量分析
Miniaturized String Sampling Probe and Electrospray Extraction/Ionization within the Ion Inlet Tube for Mass Spectrometric Endoscopy
質量分析内視鏡検査用のイオンインレットチューブ内の小型ストリングサンプリングプローブとエレクトロスプレー抽出/イオン化
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 32, 2, 606–610

Summary
A moving string sampling probe and a new ESI based ionization source that can be readily incorporated into the existing endoscopes are developed for performing in vivo mass spectrometry during the endoscopic procedure. The medical-grade silk suture driven by a stepping motor is used to perform the sampling on the region of interest when the probe head is brought gently into contact with the surface of the gastrointestinal tissue. The tissues and the compounds adhered to the sampling string are transported to an ionization region inside the ion inlet tube in which they are extracted and ionized by the charging droplets generated from an electrospray outside the ion inlet. Since the extraction/ionization and sampling processes are isolated, organic solvents, high voltage (HV), and heating can be used for the optimization of ionization without compromising the biocompatibility of the sampling probe. The demonstration of the in vivo analysis of the gastric mucosa of a mouse is performed using a 2 m long gastrointestinal endoscope.
要旨
内視鏡手術中に生体内質量分析を実行するために、既存の内視鏡に容易に組み込むことができる可動ストリングサンプリングプローブと新しいESIベースのイオン化源が開発されています。ステッピングモーターによって駆動される医療グレードの絹の縫合糸は、プローブヘッドが胃腸組織の表面に穏やかに接触するときに、関心のある領域でサンプリングを実行するために使用されます。サンプリングストリングに付着した組織と化合物は、イオン注入口チューブ内のイオン化領域に輸送され、イオン注入口外のエレクトロスプレーから生成された帯電液滴によって抽出およびイオン化されます。抽出/イオン化およびサンプリングプロセスが分離されているため、サンプリングプローブの生体適合性を損なうことなく、有機溶媒、高電圧(HV)、および加熱を使用してイオン化を最適化できます。マウスの胃粘膜のinvivo分析のデモンストレーションは、2mの長さの胃腸内視鏡を使用して実行されます。
11. Compact HP-ESI 簡易小型高圧ESI源
High-pressure ESI-MS made easy using a plug-and-play ion source and its application to highly conductive aqueous solutions
プラグアンドプレイイオン源を使用して高圧ESI-MSを容易にし、導電性の高い水溶液への応用
Journal of Mass Spectrometry 56 (4), e4583 (2021)
Summary
The performance of a compact high-pressure electrospray ionization (HP-ESI) source that can be readily used for commercial atmospheric pressure ionization (API) mass spectrometers is reported. The ion source employs a converging–diverging outlet nozzle, and ions/droplets generated inside the high-pressure compartment are carried by the high-velocity air jet toward the mass spectrometry (MS) ion inlet placed under the atmospheric pressure. With the use of a shielding electrode, the HP-ESI can also be operated with its emitter held at ground potential. This feature prevents the flow of current from the emitter to other electrically grounded components and facilitates the connection of ion source to liquid chromatography (LC) columns or capillary electrophoresis. Sensitive detection of proteins from highly conductive aqueous solutions such as 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) solution and the prevention of electrochemical artifacts by the grounded emitter operation are demonstrated.
要旨
市販の大気圧イオン化(API)質量分析計に容易に使用できるコンパクトな高圧エレクトロスプレーイオン化(HP-ESI)ソースの性能が報告されています。 イオン源は収束-発散出口ノズルを採用し、高圧コンパートメント内で生成されたイオン/液滴は、大気圧下に配置された質量分析(MS)イオン入口に向けて高速エアジェットによって運ばれます。 HP-ESIは、シールド電極を使用することで、エミッターを接地電位に保持した状態で操作することもできます。 この機能は、エミッタから他の電気的に接地されたコンポーネントへの電流の流れを防ぎ、イオン源の液体クロマトグラフィー(LC)カラムまたはキャピラリー電気泳動への接続を容易にします。 0.1%トリフルオロ酢酸(TFA)溶液などの高導電性水溶液からのタンパク質の高感度検出と、接地されたエミッター操作による電気化学的アーチファクトの防止が実証されています。
12. High-Pressure High-Temperature MicroLC 高圧高温キャピラリーLC
A Plug-and-Play High-Pressure ESI Source with an Emitter at Ground Potential and Its Application to High-Temperature Capillary LC-MS
接地電位にエミッタを備えたプラグアンドプレイ高圧ESIソースとその高温キャピラリLC-MSへの応用
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 5, 1015–1018

Summary
A new high-pressure ESI source that can be readily used for commercial API mass spectrometers in a plug-and-play manner without any modification on the ion sampling interface is introduced. The emitter can be operated at ground potential, and the positive mode electrospray is generated by applying a negative high potential to the counter electrode. A shielding electrode effectively shields the opposing electric field and improves the ion transmission. This feature facilitates the direct connection of the ESI emitter to the electrically grounded components. The application of the present ion source to the high-temperature (>100 °C) capillary liquid chromatography for high-speed separation of peptide and proteins is demonstrated using a monolithic polymeric column.
要旨
イオンサンプリングインターフェイスを変更せずにプラグアンドプレイ方式で市販のAPI質量分析計に簡単に使用できる新しい高圧ESIソースが導入されました。エミッターは接地電位で操作でき、正モードのエレクトロスプレーは、対極に負の高電位を印加することによって生成されます。シールド電極は、反対側の電界を効果的にシールドし、イオン透過を改善します。この機能により、ESIエミッターを電気的に接地されたコンポーネントに直接接続できます。ペプチドとタンパク質の高速分離のための高温(> 100°C)キャピラリー液体クロマトグラフィーへの本イオン源の適用は、モノリシックポリマーカラムを使用して実証されています。
13. High-pressure high temperature ESI-LC-MS 高圧高温液クロ
Hyphenation of high-temperature liquid chromatography with high-pressure electrospray ionization for subcritical water LC-ESI-MS
亜臨界水用の高圧エレクトロスプレーイオン化による高温液体クロマトグラフィーのハイフネーションLC-ESI-MS
Analyst 143 (22), 5552-5558 (2018)
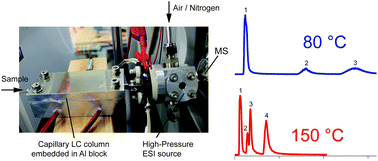
Summary
High-pressure electrospray ionization (HP-ESI) performed under super-atmospheric pressure allows a stable and efficient electrospray of pure aqueous and/or superheated solutions even under a μL min−1 flow rate regime. In this paper, we report the direct coupling of the HP-ESI source to high-temperature liquid chromatography (HT-LC) operated at ≤30 μL min−1 flow rates. In addition to ESI, the ion source functions as a back-pressure regulator to keep the mobile phase in the liquid phase when the column is heated to >100 °C. Under an ion source pressure of 7 bar, the LC column can be operated up to 160 °C. LC is performed under isocratic elution, and besides the isothermal mode, the temperature of the column can also be programmed to increase the selectivity while keeping the ion source at a constant temperature. For a given solution flow rate, the analytical time can be shortened by increasing the column temperature. HT-LC-ESI-MS using pure water as the mobile phase with a capillary column is also demonstrated.
要旨
超大気圧下で実行される高圧エレクトロスプレーイオン化(HP-ESI)により、μLmin-1の流量レジーム下でも、純粋な水溶液および/または過熱溶液の安定した効率的なエレクトロスプレーが可能になります。この論文では、HP-ESIソースと≤30μLmin-1流量で動作する高温液体クロマトグラフィー(HT-LC)の直接結合について報告します。 ESIに加えて、イオン源は背圧レギュレーターとして機能し、カラムが100°Cを超えるまで加熱されたときに移動相を液相に保ちます。 7 barのイオン源圧力下で、LCカラムは160°Cまで操作できます。 LCはアイソクラティック溶出下で実行され、等温モードに加えて、イオン源を一定温度に保ちながら選択性を高めるようにカラムの温度をプログラムすることもできます。所定の溶液流量に対して、カラム温度を上げることで分析時間を短縮できます。キャピラリカラムを備えた移動相として純水を使用するHT-LC-ESI-MSも示されています。
14. Ultra-fast protein digestion 高速タンパク質分析
Super-atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry and its application to ultrafast online protein digestion analysis
超大気圧イオン化質量分析とその超高速オンラインタンパク質分解分析への応用
Journal of Mass Spectrometry 51 (6), 396-411 (2016)
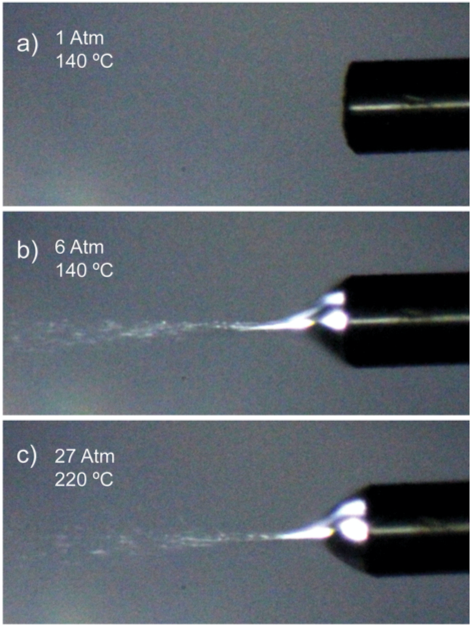
Summary
Ion source pressure plays a significant role in the process of ionization and the subsequent ion transmission inside a mass spectrometer. Pressurizing the ion source to a gas pressure greater than atmospheric pressure is a relatively new approach that aims to further improve the performance of atmospheric pressure ionization sources. For example, under a super-atmospheric pressure environment, a stable electrospray can be sustained for liquid with high surface tension such as pure water, because of the suppression of electric discharge. Even for nano-electrospray ionization (nano-ESI), which is known to work with aqueous solution, its stability and sensitivity can also be enhanced, particularly in the negative mode when the ion source is pressurized. A brief review on the development of super-atmospheric pressure ion sources, including high-pressure electrospray, field desorption and superheated ESI, and the strategies to interface these ion sources to a mass spectrometer will be given. Using a recent ESI prototype with an operating temperature at 220 °C under 27 atm, we also demonstrate that it is possible to achieve an online Asp-specific protein digestion analysis in which the whole processes of digestion, ionization and MS acquisition could be completed on the order of a few seconds. This method is fast, and the reaction can even be monitored on a near-real-time basis.
要旨
イオン源圧力は、質量分析計内でのイオン化とそれに続くイオン透過のプロセスで重要な役割を果たします。イオン源を大気圧よりも高いガス圧に加圧することは、大気圧イオン化源の性能をさらに改善することを目的とした比較的新しいアプローチです。例えば、超大気圧環境下では、放電が抑制されるため、純水などの表面張力の高い液体に対しても安定したエレクトロスプレーを維持することができます。水溶液で機能することが知られているナノエレクトロスプレーイオン化(nano-ESI)の場合でも、特にイオン源が加圧されている負モードでは、その安定性と感度を向上させることができます。高圧エレクトロスプレー、フィールド脱離、過熱ESIなどの超大気圧イオン源の開発と、これらのイオン源を質量分析計に接続するための戦略について簡単に説明します。動作温度が220°C、27 atmの最近のESIプロトタイプを使用して、消化、イオン化、MS取得の全プロセスを完了できるオンラインAsp固有のタンパク質消化分析を実現できることも示しています。数秒のオーダー。この方法は高速であり、反応をほぼリアルタイムで監視することもできます。
15. Application of high-temperature ESI 高温ESIの応用:タンパク質の非酵素消化
Rapid Online Non-Enzymatic Protein Digestion Analysis with High Pressure Superheated ESI-MS
高圧過熱ESI-MSによる迅速なオンライン非酵素的タンパク質消化分析
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 7, 1085–1091

Summary
Recently, we reported a new ESI ion source that could electrospray the super-heated aqueous solution with liquid temperature much higher than the normal boiling point (J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom.25, 1862–1869). The boiling of liquid was prevented by pressurizing the ion source to a pressure greater than atmospheric pressure. The maximum operating pressure in our previous prototype was 11 atm, and the highest achievable temperature was 180°C. In this paper, a more compact prototype that can operate up to 27 atm and 250°C liquid temperatures is constructed, and reproducible MS acquisition can be extended to electrospray temperatures that have never before been tested. Here, we apply this super-heated ESI source to the rapid online protein digestion MS. The sample solution is rapidly heated when flowing through a heated ESI capillary, and the digestion products are ionized by ESI in situ when the solution emerges from the tip of the heated capillary. With weak acid such as formic acid as solution, the thermally accelerated digestion (acid hydrolysis) has the selective cleavage at the aspartate (Asp, D) residue sites. The residence time of liquid within the active heating region is about 20 s. The online operation eliminates the need to transfer the sample from the digestion reactor, and the output of the digestive reaction can be monitored and manipulated by the solution flow rate and heater temperature in a near real-time basis.
要旨
最近、通常の沸点よりもはるかに高い液体温度で過熱水溶液をエレクトロスプレーできる新しいESIイオン源を報告しました(J.Am。Soc。MassSpectrom.25、1862–1869)。イオン源を大気圧より高い圧力に加圧することにより、液体の沸騰を防いだ。以前のプロトタイプの最大動作圧力は11atmで、達成可能な最高温度は180°Cでした。この論文では、最大27 atmおよび250°Cの液体温度で動作できるよりコンパクトなプロトタイプを構築し、再現性のあるMS取得を、これまでテストされたことのないエレクトロスプレー温度に拡張できます。ここでは、この過熱ESIソースを高速オンラインタンパク質分解MSに適用します。サンプル溶液は、加熱されたESIキャピラリーを流れるときに急速に加熱され、分解生成物は、溶液が加熱されたキャピラリーの先端から出てくるときに、ESIによってその場でイオン化されます。溶液としてギ酸などの弱酸を使用すると、熱的に加速された消化(酸加水分解)は、アスパラギン酸(Asp、D)残基部位で選択的に切断されます。アクティブ加熱領域内の液体の滞留時間は約20秒です。オンライン操作により、分解反応器からサンプルを移送する必要がなくなり、消化反応の出力をほぼリアルタイムで溶液の流量とヒーター温度によって監視および操作できます。
16. 高圧高温ESI
High Pressure Super-Heated Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Sub-Critical Aqueous Solution
高圧超加熱エレクトロスプレーイオン化を用いた亜臨界水溶液の質量分析
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 25, 11, 1862–1869

Summary
The heating of electrospray ion source under atmospheric pressure is limited to the normal boiling point of the solution. The boiling takes place when the vapor pressure of the liquid at a given temperature equals the ambient pressure. By using a high pressure ESI source, which has been developed previously in our laboratory, a stable electrospray ionization of super-heated aqueous solution is performed up to a solution temperature of 180°C. The ion source is pressurized with pure nitrogen to a maximum pressure of 11 atm, and it is coupled to a commercial mass spectrometer via a custom-made ion transport capillary. A booster pump with variable pumping speed is added to the pumping system to regulate the pressure in the first pumping stage at 1 ~ 1.3 Torr. High pressure mass spectrometry is performed on several peptides and proteins to demonstrate its application in the temperature-controlled thermally induced denaturation and dissociation.
要旨
大気圧下でのエレクトロスプレーイオン源の加熱は、溶液の通常の沸点に制限されます。 沸騰は、特定の温度での液体の蒸気圧が周囲圧力に等しいときに発生します。 私たちの研究室で以前に開発された高圧ESIソースを使用することにより、180°Cの溶液温度まで過熱水溶液の安定したエレクトロスプレーイオン化が実行されます。 イオン源は純窒素で最大圧力11atmに加圧され、カスタムメイドのイオン輸送キャピラリーを介して市販の質量分析計に結合されます。 可変ポンプ速度のブースターポンプがポンプシステムに追加され、最初のポンプ段階の圧力を1〜1.3Torrに調整します。 高圧質量分析は、温度制御された熱的に誘発された変性および解離におけるその応用を実証するために、いくつかのペプチドおよびタンパク質に対して実行されます。
17. Rear extractor 後方対向電極
Electrospray ionization source with a rear extractor
後方対向電極を用いたエレクトロスプレーイオン源
J. Mass Spectrom. 53, 400-407 (2018)

Summary
A new electrospray source design is introduced by having an extractor electrode placed at 1 to 2 mm behind the emitter tip. The extractor was integrated into the sprayer body as a single device. An insulating tube was used to isolate the emitter from the extractor and to deliver the sheath gas for the electrospray. The electric field strength at the emitter was primarily determined by the relative position and the potential between the needle and the extractor; therefore, the spraying condition was insusceptible to the change of sprayer position or orientation with respect to the ion sampling inlet. Such design allowed the use of much lower operating voltage and facilitated the optimization of sprayer position by keeping the electric field parameter constant. Using an emitter capillary of 150 and 310 μm in inner and outer diameters, strong ion signal could still be acquired with 2-kV emitter potential even if the distance between the emitter and ion inlet was extended to >70 mm. Charge reduction of protein ions using 2 extractor-based electrosprays of opposite emitter polarities was also demonstrated.
要旨
新しいエレクトロスプレーソースの設計は、エミッターの先端の1〜2mm後ろに抽出電極を配置することによって導入されます。抽出器は、単一のデバイスとして噴霧器本体に統合されました。エミッターを抽出器から隔離するために絶縁管が使用され、エミッターでの電界強度は、主に針と抽出器の間の相対位置と電位によって決定されました。したがって、噴霧条件は、内径および外径が150および310μmのエミッタキャピラリを使用することに関して、噴霧器の位置または向きの変化の影響を受けませんでしたが、それでも強いイオン信号が発生する可能性があります。このような設計により、はるかに低い動作電圧の使用が可能になり、電界パラメータを一定に保つことで噴霧器の位置の最適化が容易になりました。エミッタとイオン注入口の間の距離が> 70 mmに拡張された場合でも、2kVのエミッタ電位で取得されます。反対のエミッタ極性の2つの抽出器ベースのエレクトロスプレーを使用したタンパク質イオンの電荷還元も実証されました。
18. Remote Sampling ESI: Application
Real-time analysis of living animals and rapid screening of human fluid samples using remote sampling electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
リモートサンプリングエレクトロスプレーイオン化質量分析を使用した生きた動物のリアルタイム分析と人体液サンプルの迅速なスクリーニング
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, Volume 172, 5 August 2019, Pages 372-378


Summary
Real-time and in-situ mass-spectrometry analyses of living animal and biological sample were performed using a novel remote sampling electrospray ionization (RS-ESI) probe. Unlike conventional ESI, in which injection or syringe loading is required for sample introduction, the RS-ESI probe ionizes the samples when the sampling capillary is in contact with the sample. As the sampling capillary is electrically held at ground potential, the safety of the animal and operator is assured. The liquid sample is aspirated to the ESI emitter at the other end of the capillary by the Venturi effect. Subsequently, the electrospray is generated when a high voltage is applied to the counter electrode placed inside the ion source chamber. The probe unit is attached to the mass spectrometer with a long flexible tube and its position can be freely manipulated during the analysis. In this report, we demonstrate a real-time analysis of a living mouse liver and an automatic analysis of 138 serum samples using this new technique.
要旨
新しいリモート サンプリング エレクトロスプレー イオン化 (RS-ESI) プローブを使用して、生きた動物および生物学的サンプルのリアルタイムおよびその場質量分析分析を実行しました。 サンプルの導入に注入またはシリンジの装填が必要な従来の ESI とは異なり、RS-ESI プローブは、サンプリング キャピラリーがサンプルと接触しているときにサンプルをイオン化します。 サンプリングキャピラリーは電気的に接地電位に保持されているため、動物とオペレーターの安全が保証されます。 液体サンプルは、ベンチュリ効果によってキャピラリーの他端にある ESI エミッターに吸引されます。 続いて、イオン源チャンバー内に設置された対向電極に高電圧が印加されるとエレクトロスプレーが発生します。 プローブユニットは長いフレキシブルチューブで質量分析計に取り付けられており、分析中にその位置を自由に操作できます。 このレポートでは、この新しい技術を使用した生きたマウス肝臓のリアルタイム分析と 138 個の血清サンプルの自動分析を実証します。
19. Remote Sampling ESI: Development
Development of Remote Sampling ESI Mass Spectrometry for the Rapid and Automatic Analysis of Multiple Samples
複数サンプルの迅速かつ自動分析のためのリモート サンプリング ESI 質量分析法の開発
Mass Spectrometry (Tokyo), 2016, vol 5, pp S0068
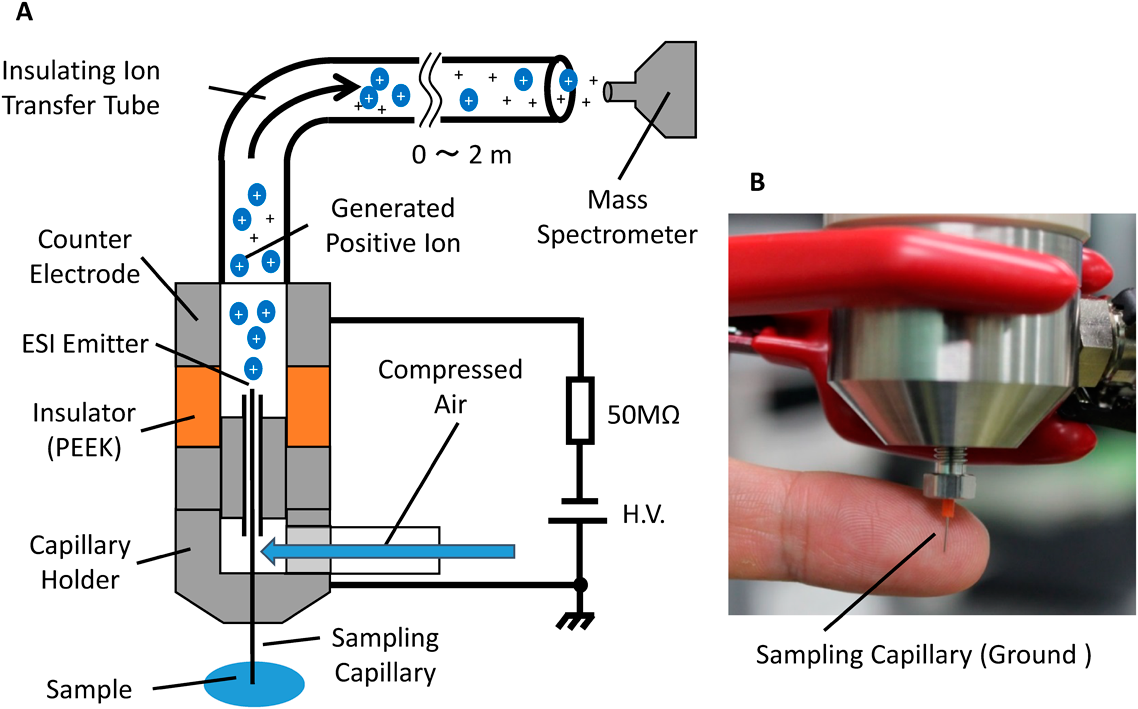
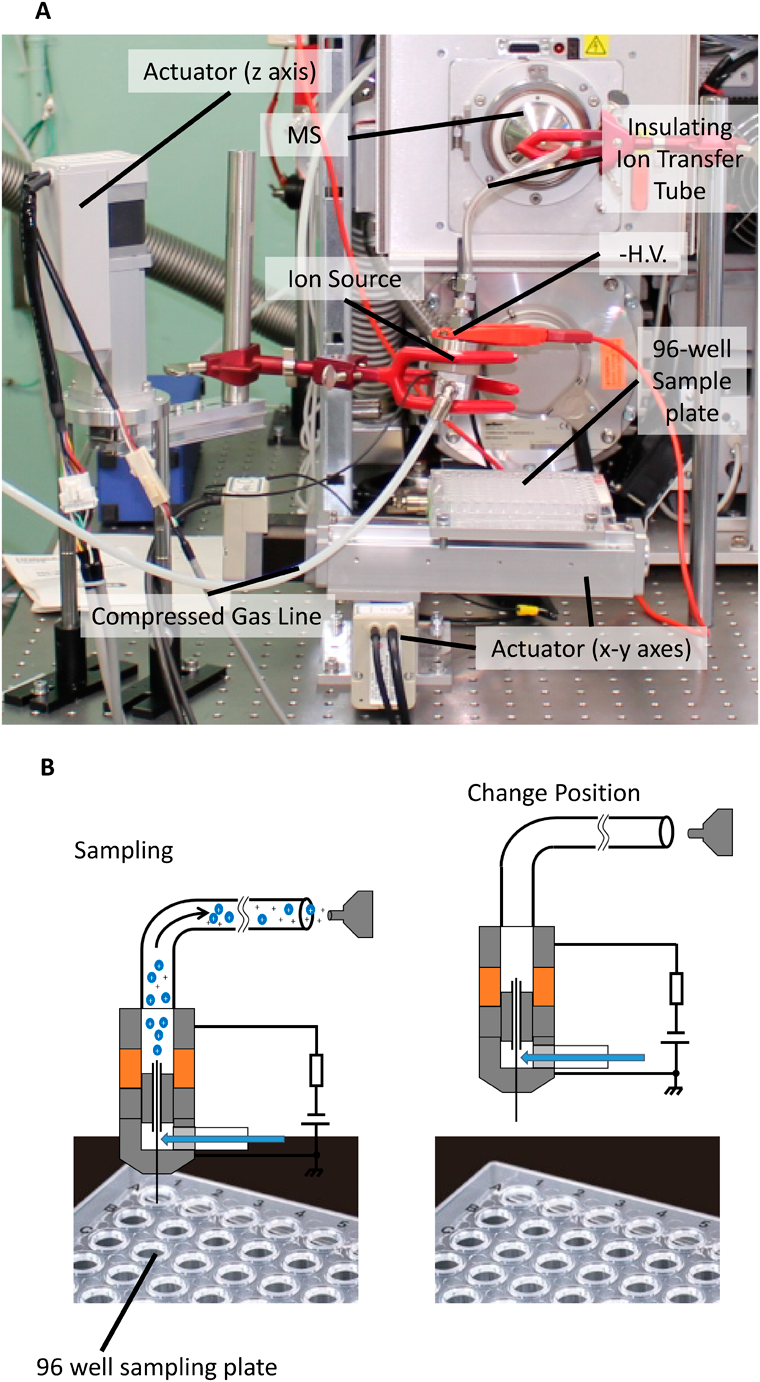

Summary
We report on combining a self-aspirated sampling probe and an ESI source using a single metal capillary which is electrically grounded and safe for use by the operator. To generate an electrospray, a negative H.V. is applied to the counter electrode of the ESI emitter to operate in positive ion mode. The sampling/ESI capillary is enclosed within another concentric capillary similar to the arrangement for a standard pneumatically assisted ESI source. The suction of the liquid sample is due to the Venturi effect created by the high-velocity gas flow near the ESI tip. In addition to serving as the mechanism for suction, the high-velocity gas flow also assists in the nebulization of charged droplets, thus producing a stable ion signal. Even though the potential of the ion source counter electrode is more negative than the mass spectrometer in the positive ion mode, the electric field effect is not significant if the ion source and the mass spectrometer are separated by a sufficient distance. Ion transmission is achieved by the viscous flow of the carrier gas. Using the present arrangement, the user can hold the ion source in a bare hand and the ion signal appears almost immediately when the sampling capillary is brought into contact with the liquid sample. The automated analysis of multiple samples can also be achieved by using motorized sample stage and an automated ion source holder.
要旨
電気的に接地され、オペレーターが安全に使用できる単一の金属キャピラリーを使用して、自己吸引サンプリングプローブと ESI ソースを組み合わせる方法について報告します。 エレクトロスプレーを生成するには、負の H.V. ESIエミッタの対向電極に印加され、正イオンモードで動作します。 サンプリング/ESI キャピラリーは、標準的な空気圧補助 ESI 源の配置と同様の別の同心キャピラリー内に密閉されています。 液体サンプルの吸引は、ESI チップ付近の高速ガス流によって生成されるベンチュリ効果によるものです。 高速ガス流は、吸引機構として機能するだけでなく、帯電液滴の噴霧化にも役立ち、安定したイオン信号を生成します。 陽イオンモードでは、イオン源の対向電極の電位が質量分析計よりも負であっても、イオン源と質量分析計が十分な距離離れていれば、電場の影響は大きくありません。 イオンの透過はキャリアガスの粘性流によって行われます。 この構成を使用すると、ユーザーはイオン源を素手で持つことができ、サンプリングキャピラリーが液体サンプルと接触するとほぼ即座にイオン信号が現れます。 複数のサンプルの自動分析は、電動サンプルステージと自動イオン源ホルダーを使用して実現することもできます。